mirror of
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer.git
synced 2025-09-29 13:25:09 +00:00
Merge #283
283: Docs r=matklad a=matklad Co-authored-by: Aleksey Kladov <aleksey.kladov@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
commit
fd22dbde20
1 changed files with 65 additions and 25 deletions
|
|
@ -4,6 +4,33 @@ This document describes high-level architecture of rust-analyzer.
|
||||||
If you want to familiarize yourself with the code base, you are just
|
If you want to familiarize yourself with the code base, you are just
|
||||||
in the right place!
|
in the right place!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
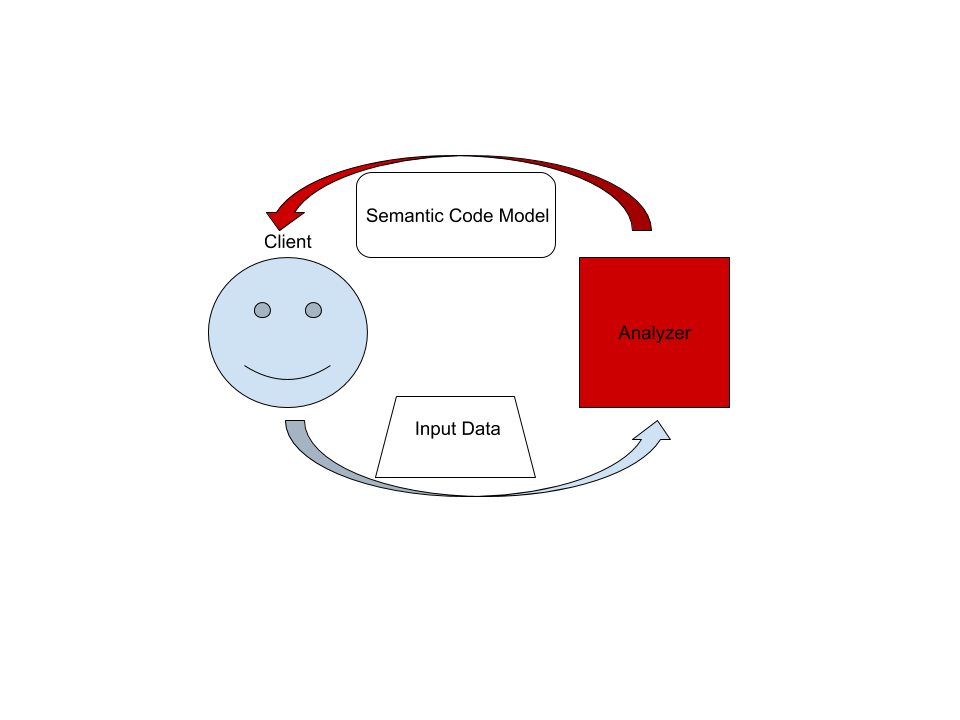
## The Big Picture
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
On the highest level, rust-analyzer is a thing which accepts input source code
|
||||||
|
from the client and produces a structured semantic model of the code.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
More specifically, input data consists of a set of test files (`(PathBuf,
|
||||||
|
String)` pairs) and an information about project structure, the so called
|
||||||
|
`CrateGraph`. Crate graph specifies which files are crate roots, which cfg flags
|
||||||
|
are specified for each crate (TODO: actually implement this) and what are
|
||||||
|
dependencies between the crate. The analyzer keeps all these input data in
|
||||||
|
memory and never does any IO. Because the input data is source code, which
|
||||||
|
typically measures in tens of megabytes at most, keeping all input data in
|
||||||
|
memory is OK.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A "structured semantic model" is basically an object-oriented representations of
|
||||||
|
modules, functions and types which appear in the source code. This representation
|
||||||
|
is fully "resolved": all expressions have types, all references are bound to
|
||||||
|
declarations, etc.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The client can submit a small delta of input data (typically, a change to a
|
||||||
|
single file) and get a fresh code model which accounts for changes.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Underlying engine makes sure that model is computed lazily (on-demand) and can
|
||||||
|
be quickly updated for small modifications.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Code generation
|
## Code generation
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -58,14 +85,47 @@ all `//test test_name` comments into files inside `tests/data` directory.
|
||||||
See [#93](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/93) for an example PR which
|
See [#93](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/93) for an example PR which
|
||||||
fixes a bug in the grammar.
|
fixes a bug in the grammar.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### `crates/ra_db`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We use [salsa][https://github.com/salsa-rs/salsa] crate for incremental and
|
||||||
|
on-demand computation. Roughly, you can think of salsa as a key-value store, but
|
||||||
|
it also can compute derived values using specified functions. The `ra_db` crate
|
||||||
|
provides a basic infrastructure for interracting with salsa. Crucially, it
|
||||||
|
defines most of the "input" queries: facts supplied by the client of the analyzer.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/ra_hir`
|
### `crates/ra_hir`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
HIR (previsouly known as descriptors) provides a high-level OO acess to Rust
|
HIR provides a high-level "object oriented" acess to Rust code.
|
||||||
code.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The principal difference between HIR and syntax trees is that HIR is bound
|
The principal difference between HIR and syntax trees is that HIR is bound to a
|
||||||
to a particular crate instance. That is, it has cfg flags and features
|
particular crate instance. That is, it has cfg flags and features applied (in
|
||||||
applied. So, there relation between syntax and HIR is many-to-one.
|
theory, in practice this is to be implemented). So, there relation between
|
||||||
|
syntax and HIR is many-to-one. The `source_binder` modules is responsible for
|
||||||
|
guessing a hir for a particular source position.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Underneath, hir works on top of salsa, using a `HirDatabase` trait.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### `crates/ra_analysis`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
A stateful library for analyzing many Rust files as they change.
|
||||||
|
`AnalysisHost` is a mutable entity (clojure's atom) which holds
|
||||||
|
current state, incorporates changes and handles out `Analysis` --- an
|
||||||
|
immutable consistent snapshot of world state at a point in time, which
|
||||||
|
actually powers analysis.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
One interesting aspect of analysis is its support for cancellation. When a change
|
||||||
|
is applied to `AnalysisHost`, first all currently active snapshots are
|
||||||
|
cancelled. Only after all snapshots are dropped the change actually affects the
|
||||||
|
database.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### `crates/ra_lsp_server`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
An LSP implementation which uses `ra_analysis` for managing state and
|
||||||
|
`ra_editor` for actually doing useful stuff.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
See [#79](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/79/) as an
|
||||||
|
example of PR which adds a new feature to `ra_editor` and exposes it
|
||||||
|
to `ra_lsp_server`.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/ra_editor`
|
### `crates/ra_editor`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
@ -80,26 +140,6 @@ syntax tree as an input.
|
||||||
The tests for `ra_editor` are `#[cfg(test)] mod tests` unit-tests spread
|
The tests for `ra_editor` are `#[cfg(test)] mod tests` unit-tests spread
|
||||||
throughout its modules.
|
throughout its modules.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/ra_analysis`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A stateful library for analyzing many Rust files as they change.
|
|
||||||
`AnalysisHost` is a mutable entity (clojure's atom) which holds
|
|
||||||
current state, incorporates changes and handles out `Analysis` --- an
|
|
||||||
immutable consistent snapshot of world state at a point in time, which
|
|
||||||
actually powers analysis.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/ra_db`
|
|
||||||
This defines basic database traits. Concrete DB is defined by ra_analysis.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/ra_lsp_server`
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
An LSP implementation which uses `ra_analysis` for managing state and
|
|
||||||
`ra_editor` for actually doing useful stuff.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
See [#79](https://github.com/rust-analyzer/rust-analyzer/pull/79/) as an
|
|
||||||
example of PR which adds a new feature to `ra_editor` and exposes it
|
|
||||||
to `ra_lsp_server`.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### `crates/gen_lsp_server`
|
### `crates/gen_lsp_server`
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
A language server scaffold, exposing a synchronous crossbeam-channel based API.
|
A language server scaffold, exposing a synchronous crossbeam-channel based API.
|
||||||
|
|
|
||||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue