mirror of
https://github.com/astral-sh/uv.git
synced 2025-10-17 05:47:45 +00:00
This PR adds a new integrations doc page for using uv with [Coiled](https://coiled.io/). It's a slightly adapted version of this blog post https://docs.coiled.io/blog/uv-coiled-cloud-scripts.html Side note: it's been really pleasant using uv and Coiled together recently cc @zanieb for visibility --------- Co-authored-by: Zanie Blue <contact@zanie.dev>
142 lines
4.5 KiB
Markdown
142 lines
4.5 KiB
Markdown
---
|
|
title: Using uv with Coiled
|
|
description:
|
|
A complete guide to using uv with Coiled to manage Python dependencies and deploy serverless
|
|
scripts.
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
# Using uv with Coiled
|
|
|
|
[Coiled](https://coiled.io?utm_source=uv-docs) is a serverless, UX-focused cloud computing platform
|
|
that makes it easy to run code on cloud hardware (AWS, GCP, and Azure).
|
|
|
|
This guide shows how to run Python scripts on the cloud using uv for dependency management and
|
|
Coiled for cloud deployment.
|
|
|
|
## Managing script dependencies with uv
|
|
|
|
!!! note
|
|
|
|
We'll use this concrete example throughout this guide, but any Python script can be used with
|
|
uv and Coiled.
|
|
|
|
We'll use the following script as an example:
|
|
|
|
```python title="process.py" hl_lines="1-8"
|
|
# /// script
|
|
# requires-python = ">=3.12"
|
|
# dependencies = [
|
|
# "pandas",
|
|
# "pyarrow",
|
|
# "s3fs",
|
|
# ]
|
|
# ///
|
|
|
|
import pandas as pd
|
|
|
|
df = pd.read_parquet(
|
|
"s3://coiled-data/uber/part.0.parquet",
|
|
storage_options={"anon": True},
|
|
)
|
|
print(df.head())
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The script uses [`pandas`](https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/) to load a Parquet file hosted in a
|
|
public bucket on S3, then prints the first few rows. It uses
|
|
[inline script metadata](https://peps.python.org/pep-0723/) to enumerate its dependencies.
|
|
|
|
When running this script locally, e.g., with:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
$ uv run process.py
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
uv will automatically create a virtual environment and installs its dependencies.
|
|
|
|
To learn more about using inline script metadata with uv, see the
|
|
[script guide](../scripts.md#declaring-script-dependencies).
|
|
|
|
## Running scripts on the cloud with Coiled
|
|
|
|
Using inline script metadata makes the script fully self-contained: it includes the information that
|
|
is needed to run it. This makes it easier to run on other machines, like a machine in the cloud.
|
|
|
|
There are many use cases where resources beyond what's available on a local workstation are needed,
|
|
e.g.:
|
|
|
|
- Processing large amounts of cloud-hosted data
|
|
- Needing accelerated hardware like GPUs or a big machine with more memory
|
|
- Running the same script with hundreds or thousands of different inputs, in parallel
|
|
|
|
Coiled makes it simple to run code on cloud hardware.
|
|
|
|
First, authenticate with Coiled using
|
|
[`coiled login`](https://docs.coiled.io/user_guide/api.html?utm_source=uv-docs#coiled-login) :
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
$ uvx coiled login
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
You'll be prompted to create a Coiled account if you don't already have one — it's free to start
|
|
using Coiled.
|
|
|
|
To instruct Coiled to run the script on a virtual machine on AWS, add two comments to the top:
|
|
|
|
```python title="process.py" hl_lines="1-2"
|
|
# COILED container ghcr.io/astral-sh/uv:debian-slim
|
|
# COILED region us-east-2
|
|
|
|
# /// script
|
|
# requires-python = ">=3.12"
|
|
# dependencies = [
|
|
# "pandas",
|
|
# "pyarrow",
|
|
# "s3fs",
|
|
# ]
|
|
# ///
|
|
|
|
import pandas as pd
|
|
|
|
df = pd.read_parquet(
|
|
"s3://coiled-data/uber/part.0.parquet",
|
|
storage_options={"anon": True},
|
|
)
|
|
print(df.head())
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
!!! tip
|
|
|
|
While Coiled supports AWS, GCP, and Azure, this example assumes AWS is being used
|
|
(see the `region` option above). If you're new to Coiled, you'll automatically have
|
|
access to a free account running on AWS. If you're not running on AWS, you can either use
|
|
a valid `region` for your cloud provider or remove the `region` line above.
|
|
|
|
The comments tell Coiled to use the official [uv Docker image](../integration/docker.md) when
|
|
running the script (ensuring uv is available) and to run in the `us-east-2` region on AWS (where
|
|
this example data file happens to live) to avoid any data egress.
|
|
|
|
To submit a batch job for Coiled to run, use
|
|
[`coiled batch run`](https://docs.coiled.io/user_guide/api.html?utm_source=uv-docs#coiled-batch-run)
|
|
to execute the `uv run` command in the cloud:
|
|
|
|
```bash hl_lines="1"
|
|
$ uvx coiled batch run \
|
|
uv run process.py
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The same process that previously ran locally is now running on a remote cloud VM on AWS.
|
|
|
|
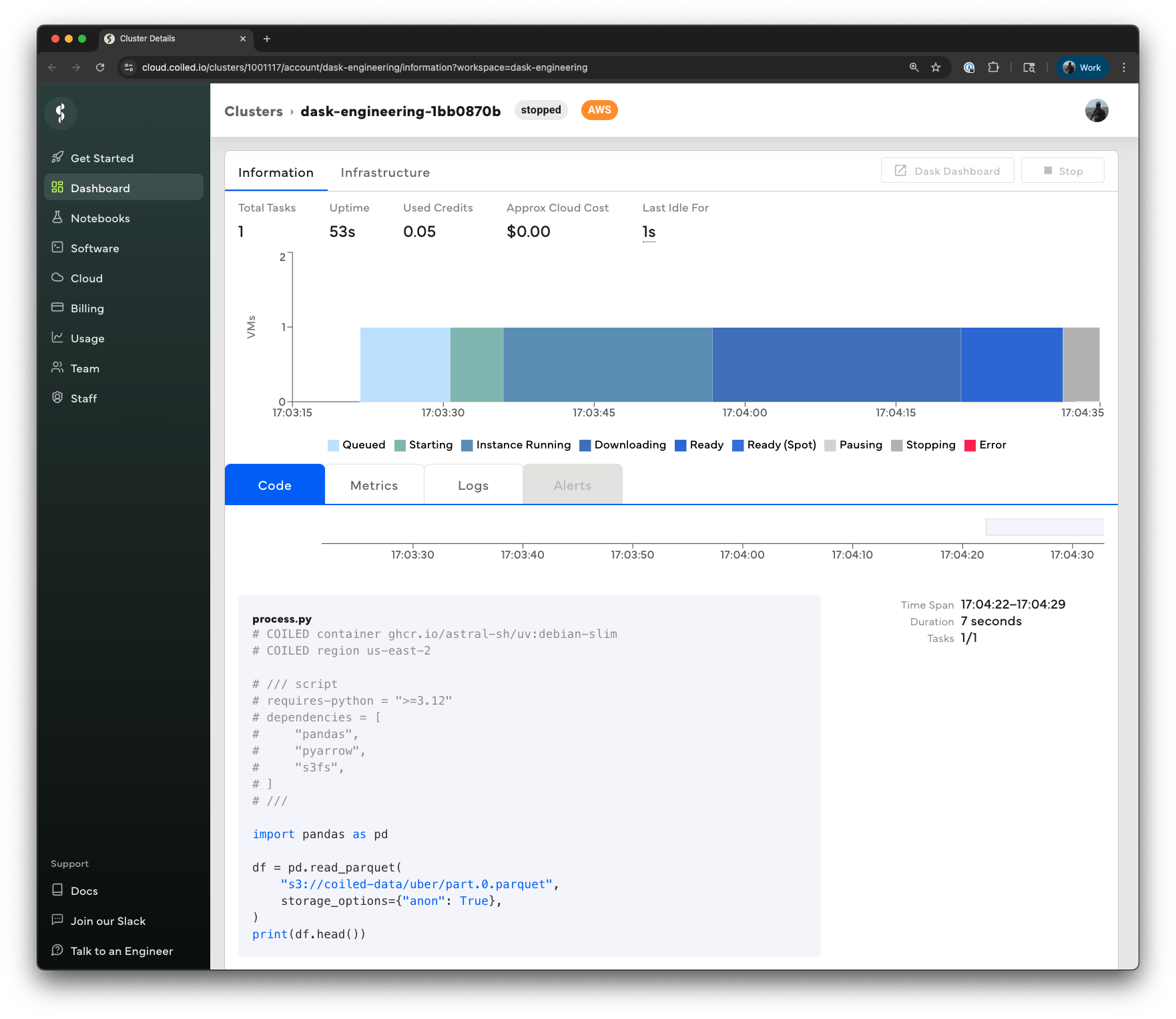
You can monitor the progress of the batch job in the UI at
|
|
[cloud.coiled.io](https://cloud.coiled.io) or from the terminal using the `coiled batch status`,
|
|
`coiled batch wait`, and `coiled batch logs` commands.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note there's additional configuration we could have specified, e.g., the instance type (the default
|
|
is a 4-core virtual machine with 16 GiB of memory), disk size, whether to use spot instance, and
|
|
more. See the
|
|
[Coiled Batch documentation](https://docs.coiled.io/user_guide/batch.html?utm_source=uv-docs) for
|
|
more details.
|
|
|
|
For more details on Coiled, and how it can help with other use cases, see the
|
|
[Coiled documentation](https://docs.coiled.io?utm_source=uv-docs).
|